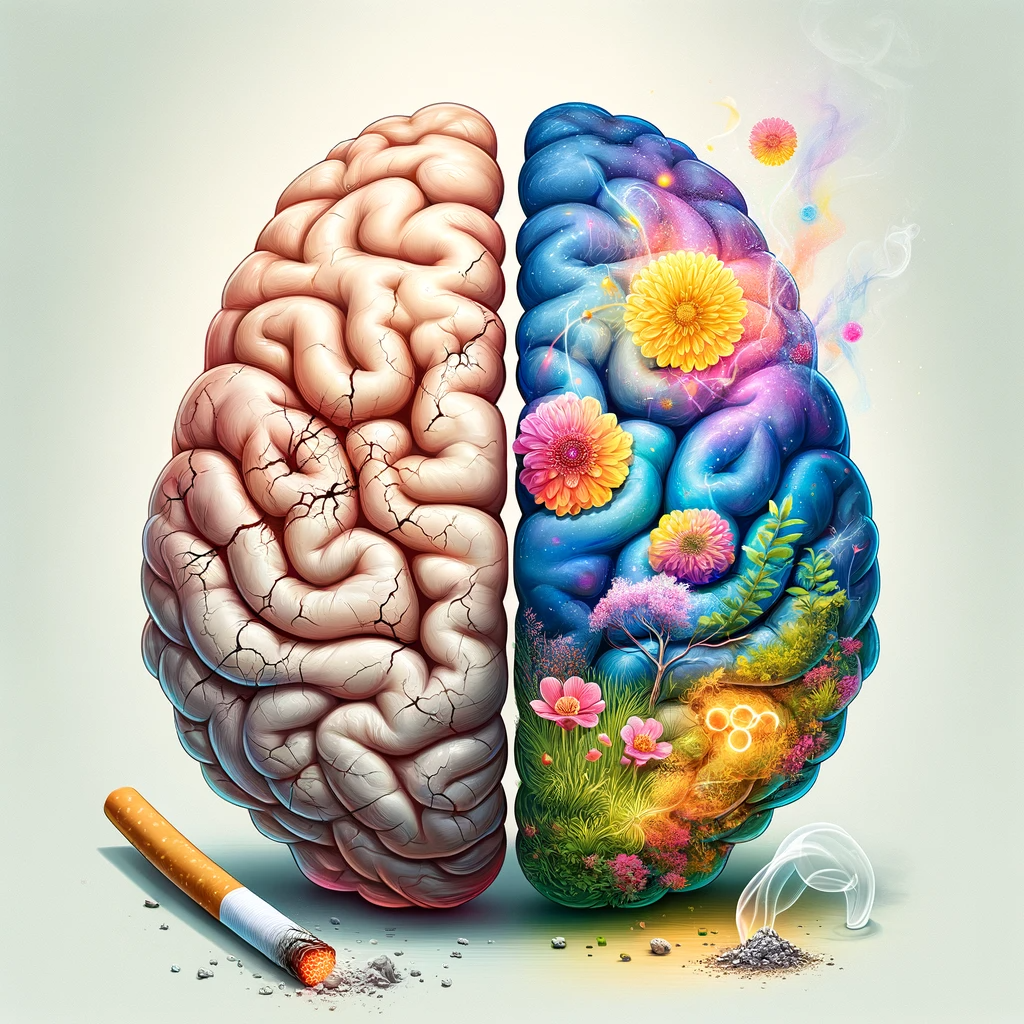
Have you ever wondered if your brain can truly recover after years of smoking? The answer is a resounding yes. Quitting smoking can lead to a remarkable transformation in your brain’s health and function.
The positive effects of quitting smoking on your brain are truly astounding, and it’s important for you to understand the dangers of smoking on your brain, as well as the incredible healing potential that comes with quitting.
In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind how your brain can heal after you quit smoking, and the steps you can take to support this process.
Key Takeaways:
- Neuroplasticity: The brain has the ability to rewire itself and heal after quitting smoking through a process called neuroplasticity. This means that the brain can create new neural pathways and recover from the damage caused by smoking.
- Improved cognitive function: Research has shown that quitting smoking can lead to improvements in memory, attention, and overall cognitive function. This is evidence of the brain’s ability to heal and recover from the negative effects of smoking.
- Time and commitment: While the brain can heal after quitting smoking, it takes time and commitment. The process of healing and rewiring the brain may not be immediate, but with dedication to a smoke-free lifestyle, individuals can experience long-term improvements in brain function.
Can Your Brain Heal After Quitting Smoking?
Neurological Effects of Smoking Cessation
Some of the most significant changes in your brain occur when you decide to quit smoking. Smoking cessation has a profound impact on your neurological health, as it can lead to improvements in cognitive function, mood regulation, and overall brain health.
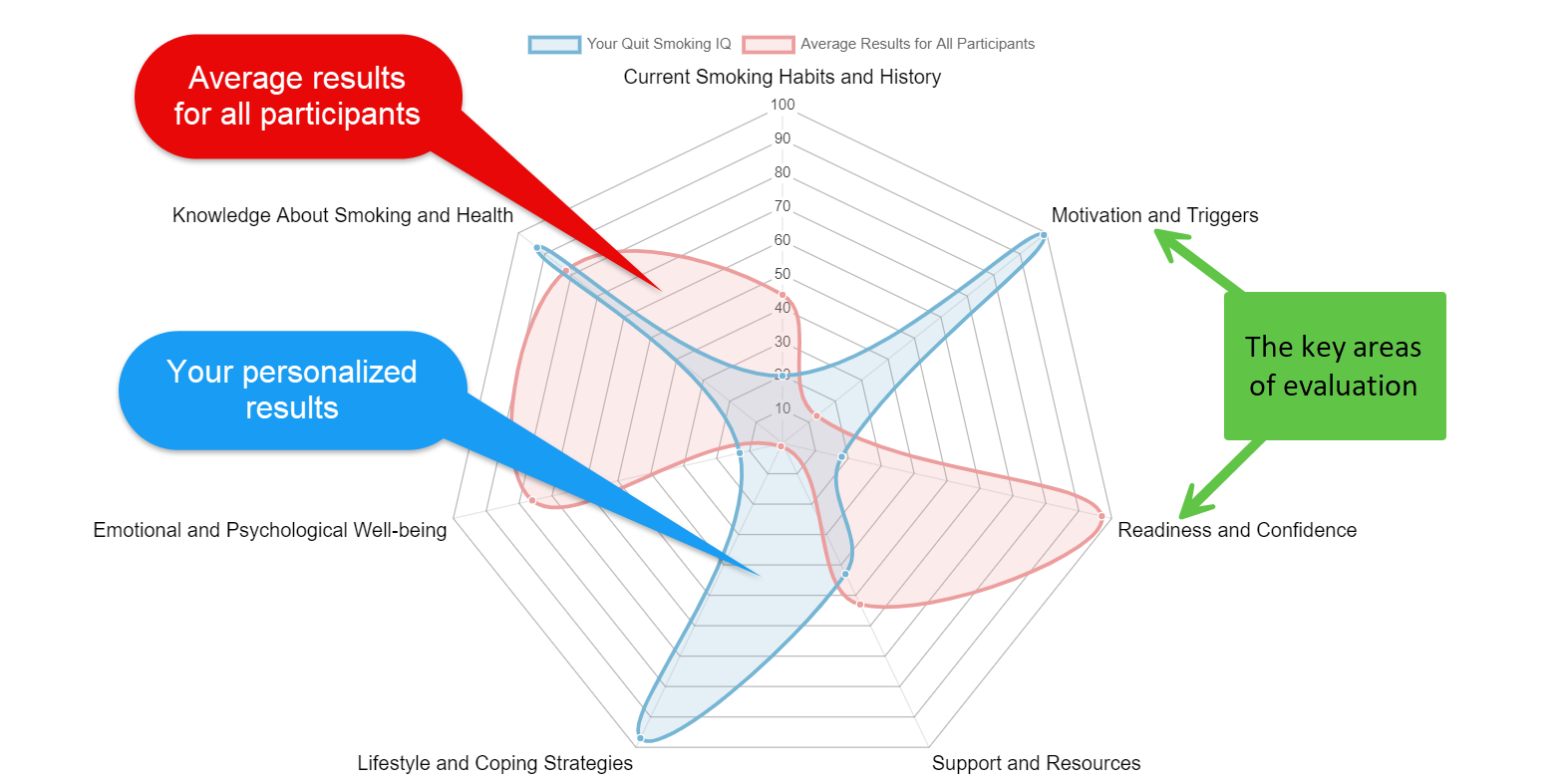
Sometimes quitting can be really tough and now you can find the reason.
Take our FREE assessment and find out what is holding you back from quitting smoking in just 60 seconds.
The neurological effects of quitting smoking are both immediate and long-term, leading to positive changes in various areas of your brain.
Immediate neurological changes upon quitting
When you quit smoking, your brain begins to undergo immediate changes. The levels of carbon monoxide in your blood drop, which increases the amount of oxygen that reaches your brain.
This can lead to improved cognitive function and mental clarity. Additionally, the nicotine receptors in your brain start to downregulate, which can initially cause withdrawal symptoms but ultimately leads to a reduction in cravings and dependence on nicotine.
You may also experience improvements in your sense of taste and smell as your neurological pathways begin to heal.
Long-term brain recovery prospects
As time goes on, your brain continues to heal and repair itself after quitting smoking. Studies have shown that the brain’s gray matter volume can start to increase once you quit smoking, particularly in areas related to memory and attention.
This means that you may experience improvements in cognitive function and information processing over time.
Furthermore, quitting smoking has been associated with a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, highlighting the long-term benefits of smoking cessation for your brain health.
Strategies to Support Brain Healing
Obviously, quitting smoking is the first step towards allowing your brain to heal from the damage caused by tobacco. However, there are additional strategies that you can implement to support this healing process.
These strategies include evidence-based approaches to quitting smoking and lifestyle changes that promote neuroregeneration.
Evidence-based approaches to quitting smoking
When it comes to quitting smoking, it’s important to rely on evidence-based approaches that have been proven to be effective.
This may include the use of nicotine replacement therapies, such as patches, gum, and lozenges, as well as prescription medications like bupropion or varenicline. Counseling and support groups can also be valuable tools in helping you overcome nicotine addiction.
It’s crucial to remember that quitting smoking is a challenging process, but with the right support and tools, you can increase your chances of success.
Lifestyle changes that promote neuroregeneration
Aside from quitting smoking, there are certain lifestyle changes that can promote neuroregeneration and support the healing of your brain.
Regular physical exercise has been shown to have a positive impact on brain health, helping to improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline. Additionally, focusing on a diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins can provide your brain with the nutrients it needs to repair and regenerate.
Getting an adequate amount of sleep, managing stress levels, and engaging in mentally stimulating activities are also important for supporting brain healing after quitting smoking.
Mental Health Implications
Unlike physical health, the mental health implications of smoking cessation may not be immediately apparent. However, quitting smoking can have a profound impact on your mental well-being.
Research has shown that individuals who quit smoking experience improvements in mood, stress levels, and overall mental health. This is because smoking cessation can lead to a reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as an increase in positive emotions and overall life satisfaction.
Additionally, quitting smoking can improve your cognitive function, including your ability to concentrate and remember information.
Psychological challenges during recovery
During the recovery process, you may experience psychological challenges such as cravings, irritability, and mood swings. These symptoms are often a result of nicotine withdrawal, as your brain adjusts to functioning without the presence of nicotine.
It’s important to remember that these psychological challenges are temporary and will diminish over time as your brain and body adapt to being smoke-free.
In the meantime, it’s important to be patient with yourself and seek support from friends, family, or a healthcare professional.
Coping mechanisms and support systems
As you navigate the psychological challenges of smoking cessation, it’s important to have coping mechanisms and support systems in place to help you manage your mental well-being.
Engaging in activities that you enjoy, such as exercise, hobbies, or spending time with loved ones, can help distract you from cravings and improve your mood.
Additionally, seeking support from others who have quit smoking or joining a support group can provide you with encouragement and accountability as you work towards maintaining your smoke-free lifestyle.
Remember that the mental health implications of quitting smoking can be significant, but the long-term benefits of improved mood, stress levels, and cognitive function make the journey towards a smoke-free life well worth it.
Studies and Statistics
Despite the addictive nature of nicotine, your brain has an incredible capacity for recovery after you quit smoking.
Numerous studies have shown that your brain can heal and regain normal functioning, even after long-term tobacco use.
Understanding the research and statistics behind the recovery process can provide you with valuable insights and motivation to stay smoke-free.
Research insights on neural recovery from nicotine addiction
Research has revealed that the brain undergoes significant changes during nicotine addiction, but these changes are not permanent.
When you quit smoking, your brain begins to repair and rewire itself, leading to improvements in cognitive functions, mood regulation, and overall mental well-being.
Studies have shown that within just a few weeks of quitting, you can experience increased blood flow to the brain, improved memory and concentration, and reduced feelings of anxiety and depression.
Comparative analysis of recovery timelines
Comparative analysis of recovery timelines shows that the extent and speed of neural recovery can vary from person to person. Factors such as the duration and intensity of smoking, age, overall health, and genetic predisposition can influence the recovery process.
However, the overall trend is clear – the longer you stay smoke-free, the more your brain will continue to heal and function at its best. Consider the following comparative analysis of recovery timelines:
Recovery Milestone Timelines
Improved blood flow to the brain
Within 2 to 12 weeks after quitting
Restored cognitive functions
Up to 3 months after quitting
Reduced risk of anxiety and depression
After 6 months of being smoke-free
Complete neural recovery
Between 1 to 2 years after quitting
Remember, your decision to quit smoking is the first and most important step towards allowing your brain to heal and thrive.
The statistics and research clearly show that your brain has the remarkable ability to recover from the damages caused by smoking, and the longer you stay smoke-free, the more you can expect to benefit from the positive changes taking place in your brain.
Stay committed to your quit journey, and give your brain the opportunity to heal and regain its full potential.
Can your brain heal after quitting smoking?
Taking this into account, yes, your brain can heal after quitting smoking. Research has shown that certain cognitive functions, such as memory and attention, can improve after you stop smoking.
Your brain’s neuroplasticity allows it to rewire and repair damage caused by smoking. As time goes on, you may experience improvements in your cognitive functioning and overall brain health.
So if you’re considering quitting smoking, know that there is hope for the healing and restoration of your brain.
FAQ
Yes, the brain has an incredible ability to heal and repair itself after quitting smoking. Research shows that within just a few weeks of quitting, the brain’s dopamine receptors start to return to normal levels, resulting in improved mood and cognitive function.
The timeline for brain healing after quitting smoking varies from person to person. However, studies have shown that significant improvements in brain function can be seen within the first few months of quitting. Over time, the brain continues to repair itself, leading to improved memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function. It’s important to note that the earlier you quit smoking, the greater the potential for brain healing.
To help your brain heal after quitting smoking, it’s important to focus on overall brain health. This includes engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, getting an adequate amount of sleep, and staying mentally active. Additionally, mindfulness practices such as meditation and deep breathing can help reduce stress and support brain healing. It’s also important to avoid exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can still have negative effects on the brain.